This study was carried out to determine the effects of different plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and mycorrhizae on the growth and development from seed to seedling of Dahlia variabilis (starflower) plant, which is widely produced in the world as a cut flower and outdoor ornamental plant, and which is becoming increasingly widespread in Türkiye.
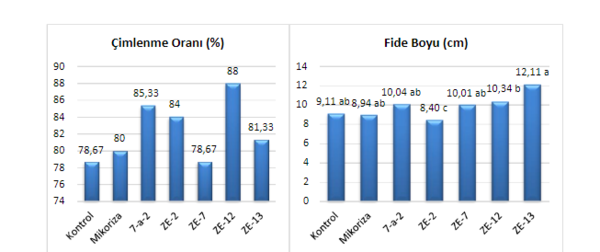 The effect of different treatments on seed germination rate and seedling height in D. variabilis. Values followed by different letters indicate that the difference between isolates is statistically significant.
The effect of different treatments on seed germination rate and seedling height in D. variabilis. Values followed by different letters indicate that the difference between isolates is statistically significant.
Within the scope of the study, Enterobacter cloacae (ZE-2), Bacillus cereus (ZE-7), Pseudomonas putida (ZE-12), Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (ZE-13), Burkholderia cepecia (7-a-2) bacterial species and commercially available mycorrhiza (5000 ppm) were applied to seeds of D. variabilis cultivar 'Violet.' To determine the effects of applications on seedling growth and development; germination rate (%), seedling height (cm), stem diameter (mm), number of leaves (piece), plant fresh weight (g), plant dry weight (g), root length (cm), root fresh weight (g), root dry weight (g) and SPAD value and chlorophyll content were measured. At the end of the study, it was determined that the applications had different effects on D. variabilis. It was determined that P. putida (ZE-12) application increased germination by 12% compared to the control, and A. calcoaceticus (ZE-13) increased the seedling height by 32.9%.
In conclusion, with this study, it was determined that these bacteria, which are of natural origin and do not harm the environment, have the potential to be used in seedling cultivation in ornamental plants, and it is important to expand the use of these applications in the ornamental plant's production sector.
Although the Dahlia plant is known in the world, there is not much information on this subject in Türkiye. In addition, the use of newly isolated bacterial species to obtain higher quality seedlings during the period from seed to seedling stage of the Dahlia plant is also very limited. Improvement of the quality of seedlings with the use of bacteria and mycorrhizae, which are among the sustainable methods, is considered to be important.
Read the complete research at: www.researchgate.net
Alkaç, Onur & Belgüzar, Sabriye & Öndeş, Esra & Okatar, Fulya & Kayaaslan, Zeliha. (2022). The Effects of Different Rhizobacteria and Mycorrhiza Applications on Seedling Growth and Development of Starflower (Dahlia variabilis). Mustafa Kemal Üniversitesi Tarım Bilimleri Dergisi. 27. 331-339.
