Digitization in agriculture is steadily growing. However, according to the Smart Agrifood Observatory, only 9.5% of Italian agricultural land is currently digitized. "Despite this marginal progress, the sector has transitioned from a few isolated sensors in the field to a wealth of data, forecasting models, regulatory requirements, and sustainability metrics in just a few years", the team with EVJA says.
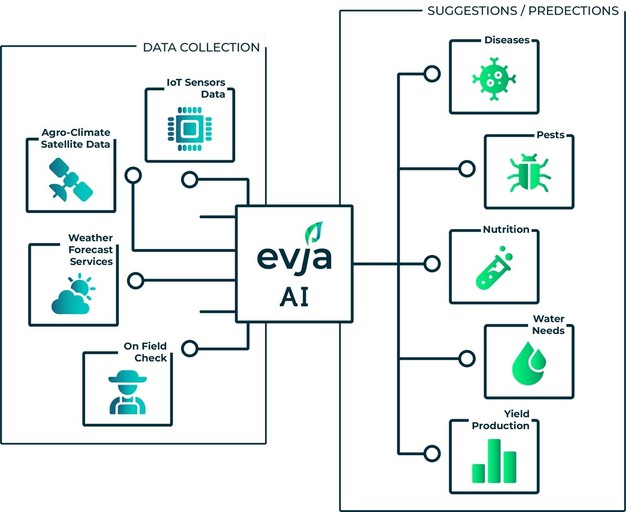
"The risk is clear. There are so many disconnected solutions, each with its own language. This increases complexity instead of simplifying the work of farmers and technicians. EVJA's Agronomic Intelligence Platform was developed precisely in response to this need. It is a unified platform for monitoring, analyzing, advocating, and ensuring sustainability by transforming complex data into actionable decisions."
 © EVJA
© EVJA
The solution in brief
The new platform has a simple yet ambitious goal, which is to facilitate data-driven agronomic decisions through a single website and application interface. "In this digital environment, farmers and technicians can access real-time monitoring of climate, soil, and crops, as well as forecasting models for major diseases, an event calendar, full data history, advanced agronomic models, yield estimation, and an updated CO₂ balance."
One of the platform's main assets is its modular design. Starting with the basic package, which includes monitoring, history, and a calendar, the platform can grow to meet the evolving needs of the farm with advanced modules such as Defense, Agronomic Modeling, Yield, and CO₂. The platform supports farms in transitioning toward more precise, sustainable, and measurable practices.
From the Basic plan to Defense: Unified monitoring and forecasting capabilities
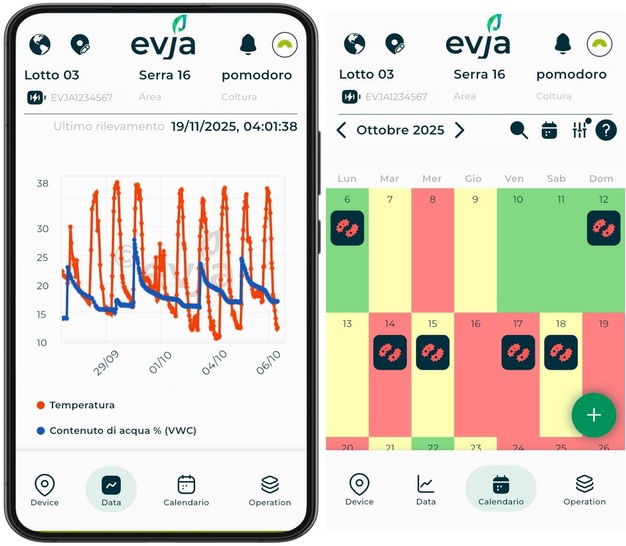
The EVJA control unit is at the heart of the Agronomic Intelligence Platform and has basic sensors. With the new app, you can view real-time graphs of soil moisture, temperature, and other climatic and crop parameters. You can also view past data organized by season, plot, or crop.
 © EVJA
© EVJA
The Defense modules are integrated into the monitoring system and include forecast models for downy mildew, alternaria, botrytis, and powdery mildew. Each model uses artificial intelligence and is fine-tuned based on user observations. The company helps optimize the models by recording adversities, treatments, and notes, making the forecasts more closely match agronomic conditions.
Agronomic models, yield, and CO₂: Turning seasonal data to business decisions
In addition to the Defense modules, the platform integrates several agronomic models, including evapotranspiration, accumulated temperature, light exposure, and chilling hours. These models allow users to track seasonal progress and plan irrigation and crop stages without relying on complex formulas.
The yield model, which is designed for leafy vegetables and castor beans, uses climate, past performance, and agronomic data to estimate expected production, crop cycle progression, and the optimal harvest window. It is a vital support tool for producer organizations and farms that need to plan labor, logistics, and contracts.
Ultimately, the CO₂ module seamlessly calculates emissions and sequestration, providing a balance that can be updated over time. This balance is a valuable reference for supply chain reports, large-scale retailer requests, and corporate ESG strategies.
 © EVJA
© EVJA
EVJA's vision
With the Agronomic Intelligence Platform, EVJA aims to transform water, defense, and sustainability management into data-driven processes without turning farms into research laboratories. The platform speaks the language of agriculture, providing information on topics such as irrigation schedules, treatment windows, yields, and CO₂ balances. It provides concrete tools that operational decision-makers can understand and use. "Innovation in the field, sustainability in the yield."
For more information: EVJA S.R.L.
EVJA S.R.L.
Via Benedetto Brin, 63
80142 Naples - Italy
+39 081 0063832
[email protected]
www.evja.eu










